Table of Contents
Introduction
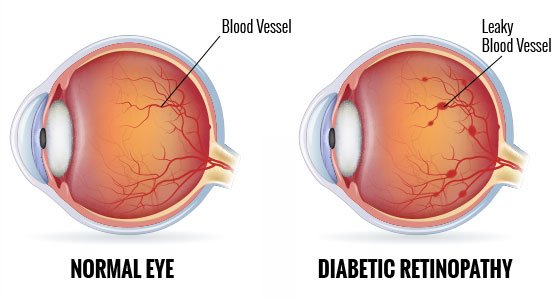
Diabetes is a chronic disease caused by an accumulation of excess glucose in the bloodstream when the body does not produce enough insulin or cannot use it properly. Uncontrolled diabetes over a long period can lead to life-threatening diseases. Diabetes can damage the heart, kidneys, nerves and eyes. Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of the eye caused by high sugar levels. The blood vessels of the light-sensitive tissues located at the back of our eyes (retina) get damaged because of diabetes in diabetic retinopathy.
In the initial stages, diabetic retinopathy might show no symptoms, but if undiagnosed at the right time, it can lead to blindness. Diabetes retinopathy is common in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The risk of diabetic retinopathy increases with uncontrolled sugar levels. A healthy diet of fruits and vegetables for diabetics is an essential method to prevent such complications.
Symptoms of diabetic retinopathy
The early stages of diabetic retinopathy might not show any signs and symptoms. But if the eye condition becomes worse, it might show the following symptoms:
- Floaters (dark strings or spots) in your vision
- Blurred vision
- Empty or dark areas in our vision
- Vision loss or blindness
- Fluctuating vision
Causes of diabetic retinopathy
With uncontrolled diabetes, the tiny blood vessels that supply blood to the retina get damaged. It leads to a lack of blood supply to the retina. Under such circumstances, the eyes try to develop new blood vessels. But the new blood vessels are weak and tend to leak easily, leading to diabetic retinopathy.
There are two types of diabetic retinopathy:
- Early diabetic retinopathy: It is also known as non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR). It is caused when new blood vessels do not grow. When we suffer from NPDR, blood and fluid leak from the weak wall of the blood vessels of our retina. NPDR can become severe when several blood vessels become blocked. Sometimes damage to the blood vessels leads to oedema, an accumulation of fluid in the centre of the retina (macula). Immediate treatment is required to prevent vision loss from macular oedema.
- Advanced diabetic retinopathy: The advanced stage of diabetic retinopathy is known as proliferative diabetic retinopathy. In this severe type of retinopathy, the old blood vessels get damaged, leading to the growth of fragile new blood vessels. The fragile blood vessels of the retina leak to accumulate in the centre of our eyes (vitreous). Consequently, scar tissues cause the retina to get detached from the back of our eyes. It leads to a build-up of pressure in our eyeball, damaging the optic nerve. Eventually, diabetic retinopathy leads to glaucoma.
Treatment of diabetic retinopathy
Treatment of diabetic retinopathy depends on whether we have early or advanced diabetic retinopathy.
Treatment of early diabetic retinopathy: If we have mild NPDR, immediate treatment is not required. The eye specialist will thoroughly check our eyes to determine the level of damage. An endocrinologist will suggest ways to keep our sugar levels under control to prevent further damage to our retina.
Treatment of advanced diabetic retinopathy: If we suffer from proliferative diabetic retinopathy or oedema, we might require urgent treatment to prevent vision loss. Depending on the level of damage, an eye specialist might suggest the following options:
- Injecting medicines into the eyes: Medicines called vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors are injected inside the vitreous of the eye to prevent further fluid build-up and growth of blood vessels. Ranibizumab, Aflibercept and Bevacizumab are used in the treatment of macular oedema.
- Photocoagulation: Also known as focal laser treatment, this can prevent the leakage of fluid and blood in our eyes. If diabetic retinopathy leads to blurred vision, laser therapy cannot reverse the situation, but it can prevent further damage.
- Vitrectomy: This surgery removes scar tissues and blood from the vitreous of our eyes. It is done in a hospital using general or local anaesthesia.
- Pan retinal photocoagulation: Also known as scatter laser treatment, this laser treatment can shrink the size of abnormal and new blood vessels.
Vegetables for diabetics
A balanced and healthy diet is essential for the management of diabetes. By controlling high blood sugar, we can prevent the onset of many diseases such as diabetic retinopathy, diabetic neuropathy and heart diseases.
Vegetables for diabetics work like a boon. Vegetables are high in fibre and nutritious and can help lower our sugar levels. Carrots, zucchini, cabbage, spinach, cucumber, tomatoes, broccoli, mushrooms, lettuce and green beans are beneficial vegetables for diabetics.
Conclusion
Eating a lot of fresh vegetables and fruits, exercising and maintaining a healthy weight can help us keep our sugar levels in control. Eating fruits low in glycemic index, non-starchy vegetables for diabetics, lean meat, whole grains and fatty fish can lower blood glucose levels. It is essential to keep our diabetes in check to avoid severe diseases in the future.